1z0-070 | Top Tips Of Renewal 1z0-070 Test Question
Examcollection 1z0-070 Questions are updated and all 1z0-070 answers are verified by experts. Once you have completely prepared with our 1z0-070 exam prep kits you will be ready for the real 1z0-070 exam without a problem. We have Renew Oracle 1z0-070 dumps study guide. PASSED 1z0-070 First attempt! Here What I Did.
Online Oracle 1z0-070 free dumps demo Below:
NEW QUESTION 1
Which three statements are true about bulk data loading capabilities in an X5 Database Machine environment?
- A. DBFS must use the DBFS_DG diskgroup for any DBFS store.
- B. DBFS may be used if Exadata-based shared storage is required to stage data before bulk loading into a database.
- C. DBFS must be used to have a POSIX-compliant shared storage solution that is accessible from the database servers on a Database Machine.
- D. DBFS must be used to bulk load data into a production database on the Database Machine.
- E. ACFS may be used if Exadata-based shared storage is required to stage data before bulk loading into a database.
- F. ACFS must be used to have a POSIX –compliant shared storage solution that is accessible from the database servers on a Database Machine.
- G. ACFS may use the DBFS_DG diskgroup to contain the ADVM volume file.
Answer: BCD
Explanation:
External tables on DBFS file-systems provide the probably the most high-performance way to bulk load data into your database.
Bulk Data Loading
Describe the various options for staging data to be bulk loading into Database Machine Configure the Database File System (DBFS) feature for staging input data files
Use external tables based on input data files stored in DBFS to perform high-performance data loads
NEW QUESTION 2
Which three statements are true about Exadata storage server alerts in an X5 Database Machine?
- A. Storage server alerts notifications may be sent using SNMP.
- B. A threshold- based alert gets cleared automatically when the measured value no longer violates the threshold.
- C. A storage server alert is only ever issued as a warning or at a critical situation.
- D. Storage server alerts are all stateless alerts.
- E. Storage server alerts are all stateful alerts.
- F. Storage server alerts notifications may be sent using SMTP.
Answer: ACF
Explanation:
Exadata cell (storage server) alerts can be delivered using SMTP or SNMP or both.
Although there are three types of storage alerts: informational, warning and critical, they are issued when threshold metrics reached either to warning or critical.
NEW QUESTION 3
You are planning your deployment of Enterprise Manager to monitor all the components of an X5 Database Machine.
A part of the requirement is to provide for high availability of the monitoring infrastructure. If the host running the agent that has Database Machine targets bound to it fails, the
monitoring of these targets must be done by another agent.
Which three statements are true regarding the configuration used to support this requirement?
- A. Database Machine plug-ins must be deployed to at least two Enterprise Manager agents.
- B. Fail back to the original agent when the host is restarted is done automatically.
- C. Fail over to any secondary agent is done automatically.
- D. Fail over to any secondary agent must be done manually.
- E. Database machine plug-ins must be deployed to all Enterprise Manager agents.
- F. Fail back to the original agent when the host is restarted must be done manually.
Answer: BCE
NEW QUESTION 4
Which three factors should you consider when choosing a method for migrating a database to the X5 Database Machine?
- A. The down time allowed for the migration
- B. Endian format of the source database
- C. Number of tablespaces in the source database
- D. The type of database workloads
- E. Size of the source database
Answer: BDE
Explanation:
B: Endian format: Non-Exadata format
D: Use Real Production Workload
– Real Application Testing (RAT) References:
NEW QUESTION 5
Which three are true concerning Storage Indexes?
- A. A maximum of eight table columns for any table are indexed per storage region.
- B. The use of Storage Indexes for particular categories of I/O can be displayed by using an I/O Resource Manager Category Plan.
- C. Storage Indexes persist across any Exadata storage server reboots.
- D. The use of Storage Indexes for a particular database can be disabled by using an I/O Resource Manager Database Plan.
- E. A Storage Index is automatically maintained by CELLSRV based on the filter columns of the offloaded SQL.
- F. Different storage regions may have different columns indexed for the same table.
Answer: ADE
Explanation:
A: Each disk in the Exadata storage cell is divided into equal sized pieces called storage regions (default 1MB). There is an index entry for every storage regions (1MB of data stored on disk). Each entry contains the minimum and maximum value for columns seen in ‘where’ clause predicates. Information for up to 8 columns can be stored. The index is then used to eliminate disk IO by identifying which storage regions don’t match the ‘where’ clause of a query.
NEW QUESTION 6
Which three must be true for a Smart Scan to occur for a table?
- A. cell_offload_processing must be true in sessions issuing SQL statements that access the table.
- B. The query must be executed serially.
- C. The query must be executed in parallel.
- D. Direct path reads must be used at run time.
- E. The ASM diskgroup containing the table’s tablespace must have a 4 Mbyte AU size.
- F. The ASM diskgroup containing the table’s tablespace must have cell.smart_scan_capable set to true.
Answer: ADF
Explanation:
A: pt_param( ‘cell_offload_processing’ ’TRUE’) hint is used to enable the exadata smart scan feature in sql execution process.
D: Direct reads bypass the buffer cache and go directly into the process PGA. Cell offload operations occur for direct reads only.
F: The cell.smart_scan_capable attribute must be set to TRUE.
NEW QUESTION 7
Which three storage components are available after nonvirtualized standard deployment of an X5 Database Machine using high-capacity disks?
- A. mirrored system area on hard disk 0, hard disk 1, and hard disk 2
- B. Exadata Smart Flash Cache using all of the flashdisk space
- C. the DBFS_DG diskgroup with high redundancy
- D. mirrored system area on hard disk 0 and hard disk 1
- E. the RECO_<DBM_Name> ASM diskgroup
- F. the DATA_<DBM_Name> ASM diskgroup
Answer: CEF
Explanation:
The first two disks of Exadata Storage Server are system disks. Oracle Exadata Storage Server Software system software resides on a portion of each of the system disks. These portions on both system disks are referred to as the system area.
The default configuration on Exadata is to have 3 diskgroups - DATA, RECO, and DBFS_DG.
NEW QUESTION 8
Which two statements are true about the use of Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) on an X5 or X6 Database Machine?
- A. IPMI can be used for server configuration and management on each database server.
- B. The Baseboard Management Controller (BMC), which supports IPMI, runs as amultithreaded process on the storage server O/S.
- C. The Baseboard Management Controller (BMC), which supports IPMI, runs as a single- threaded process on the storage server O/S.
- D. IPMI can be used for server configuration and management on each storage server.
Answer: AC
Explanation:
A: IPMI – short for Intelligent Platform Management Interface – is an interface standard that allows remote management of a server from another using standardized interface. The servers in the Exadata Database Machine follow that. It’s not an Exadata command but rather a general Linux one.
To power on a cell or database server, issue this from another server:
# ipmitool -H prolcel01-ilom -U root chassis power on
To stop a server, use the shutdown command. To stop immediately and keep it down, i.e. not reboot, execute:# shutdown -h -y now
C: Like the KCS interface, the SSIF Interface is only specified as a ‘Single Threaded Interface’ for standard IPMI commands. That is, the BMC implementation is not expected to process more than one IPMI request at a time. While an implementation is allowed to have a degree of ‘command queuing’, for standard IPMI messages the SSIF lacks a ‘Seq’ field that software can use to match up particular instances of requests with responses.
References:https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/specification-updates/ipmi-intelligent-platform-mgt-interface-spec-2nd-gen-v2-0-spec-update.pdf
NEW QUESTION 9
Which two statements are true about Auto Service Request (ASR) with an X5 Database Machine?
- A. ASR Manager must be installed and configured on a dedicated server external to the Database Machine.
- B. Configuring ASR is mandatory for all Database Machine assets.
- C. ASR Manager opens a service request (SR) automatically after sensors detect hardware faults.
- D. ASR Manager must be installed and configured on one of the database servers.
- E. ASR can upload configuration metadata to support problem resolution.
- F. ASR communicates with Oracle support services using HTTPS.
Answer: AC
Explanation:
A: Oracle recommends that you install Oracle ASR Manager on an external, standalone server.
C: Oracle ASR is designed to generate Oracle service requests automatically when certain types of faults are detected on Oracle products that are qualified for Oracle ASR.
Oracle ASR works only for specific component faults. Most of the common components, such as disks, fans, and power supplies, are covered. However, some components are not covered. For example, Oracle ASR does not cover InfiniBand events; there are specific images and specific InfiniBand switch firmware that you must use. You cannot upgrade these components independently.
NEW QUESTION 10
Which three are true concerning Exadata snapshot databases?
- A. They are supported on non-container databases.
- B. They are based on a read-write copy of an existing database.
- C. They are integrated with the Multitenant architecture.
- D. They can be created only on sparse ASM disk groups.
- E. They don’t support all Exadata features.
- F. They can be created on any type of ASM disk group.
Answer: ACD
Explanation:
A: An Exadata snapshot database can be either a non-container database (non-CDB) or a container database (CDB). Creating an Exadata snapshot database of a CDB enables access to all of the pluggable databases in that container.
C: You can create two types of Exadata snapshots, depending on the current setup of your environment:
D: SPARSE disk group based database snapshots is functionality included in Exadata Storage Software. It requires Exadata Storage Software version 12.1.2.1.0 and Oracle Database 12c version 12.1.0.2 with bundle patch 5 or later. This feature is designed to work on native Exadata ASM storage disk groups. It uses ASM SPARSE grid disk based thin provisioning where snapshot databases created on a SPARSE disk group need only the space for changes plus some metadata, thereby enabling storage efficient snapshot databases.
References:
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E80920_01/SAGUG/exadata-storage-server- snapshots.htm#SAGUG-GUID-E1D6EF45-36EF-40E3-A57E-F80B749E6122
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/exadata/learnmore/exadata-database-copy-twp-2543083.pdf
NEW QUESTION 11
Which components of an Exadata storage server image, if updated, may require that a patch also be applied to the database servers in an Exadata X6 Database Machine?
- A. Linux operating system on the storage server
- B. InfiniBand HCA firmware on the storage server
- C. Storage server hard disk device drivers
- D. Storage server flash device drivers
Answer: D
Explanation:
Exadata patches are intended for and include fixes for both the storage servers and Compute servers, and optionally InfiniBand switches.
Patching order
You should patch the Exadata Database Machines in the following sequence
References: https://www.toadworld.com/platforms/oracle/w/wiki/11640.oracle-exadata- patching
NEW QUESTION 12
You plan to migrate an existing production database supporting online transaction processing (OLTP) workloads to an X6 Exadata Database Machine.
The database currently supports an application requiring fast response times to satisfy stringent business requirements, and most of the application queries use indexed access to tables.
For which two cases would you consider dropping indexes that are not used for constraints after the migration to assure that Smart Scans occur?
- A. if Smart Scan performs better that any type of index scan on the corresponding table.
- B. if Smart only occur instead of index skip scans on the corresponding table.
- C. if Smart only occur instead of index range scans on the corresponding table.
- D. if Smart Scans performs equally well to any type of index scan on the corresponding table.
Answer: AC
NEW QUESTION 13
You plan to migrate a database supporting an OLTP workload to your new X5 Database Machine.
The current database instance supports a large number of short duration sessions and a very high volume of short transactions.
Which three X5 Database Machine features can improve performance for this type of workload?
- A. An improved highly efficient undo and redo architecture
- B. Faster optimization due to an Exadata-specific optimizer
- C. Reduced I/O latency for writes due to writeback flashcache on all Exadata X5 and later models
- D. Ultra high I/O performance for reads and writes when using Exadata Extreme Flash in X5 and later models
- E. Reduced I/O latency for reads due to read flashcache on all Exadata X5 and later models
Answer: ACD
Explanation:
A: To further accelerate OLTP workloads, the Exadata Smart Flash Cache also implements a special algorithm to reduce the latency of log write I/Os called Exadata Smart Flash Logging.
C: Use the Write-Back Flash Cache feature to leverage the Exadata Flash hardware and make Exadata Database Machine a faster system for Oracle Database Deployments.
D: Exadata X5-2 introduces Extreme Flash Storage Servers. Each Extreme Flash storage server contains eight 1.6 TB state-of-the-art PCI Flash drives. PCI flash delivers ultra-high performance by placing flash memory directly on the high speed PCI bus rather than behind slow disk controllers and directors.
References:http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/exadata/exadata-x5-2-ds- 2406241.pdf
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/articles/database/exadata-write-back-flash- 2179184.html
NEW QUESTION 14
You have partitioned an X5-2 full rack into two four-node RAC clusters called CLUSA and CLUSB.
No virtualization is used and the storage grid has not been partitioned.
Which two set of files on which servers must be modified after connecting an Exadata storage expansion rack to your X5-2 Exadata Database Machine on the InfiniBand network so that the storage servers in the expansion rack are added to the storage grid?
- A. the CELLINIT.ORA files on the database servers in CLUSA
- B. the CELLIP.ORA files on the database servers in CLUSA
- C. the CELLINIT.ORA files on the database servers in CLUSB
- D. the CELLIP.ORA files on all existing Exadata storage servers
- E. the CELLIP.ORA files on the database servers in CLUSB
- F. the CELLIP.ORA files on all newly added Exadata storage servers
Answer: BE
Explanation:
The cellip.ora is the configuration file, on every compute node (database server), that tells ASM instances which cells are available to this cluster.
The cellip.ora file contains the storage cell IP addresses. References:http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E80920_01/SAGUG/exadata-storage-server-configuring.htm#SAGUG20369
NEW QUESTION 15
Which three statements are true about the EXADCLI utility?
- A. It may be run interactively.
- B. It can be used to execute EXACLI scripts on multiple storage servers in parallel.
- C. It can be used to execute O/S commands on multiple storage servers in parallel.
- D. It can be used to execute EXACLI commands on multiple storage servers in parallel.
- E. It uses the same security mechanism as the EXACLI command.
- F. It may be used to execute DBMCLI commands on multiple database nodes in parallel.
Answer: DEF
Explanation:
The exadcli utility runs commands on multiple remote nodes in parallel threads.
You can issue an ExaCLI command to be run on multiple remote nodes. Remote nodes are referenced by their host name or IP address. Unlike dcli, exadcli can only execute ExaCLI commands. Other commands, for example, shell commands, cannot be executed using exadcli.
NEW QUESTION 16
Which two statements are true about the X5 Exadata storage server rescue procedure?
- A. The rescue procedure can be executed from the CELLBOOT USB flash drive.
- B. An Exadata storage server automatically enters the rescue environment when it cannot boot from the system area.
- C. The rescue procedure can be used to repair corruption in an ASM diskgroup.
- D. The rescue procedure can be used to restore a corrupt system area.
- E. The rescue procedure must be used to recover from a failed Exadata storage server software upgrade.
Answer: AD
Explanation:
The rescue procedure is necessary when system disks fail, the operating system has a corrupt file system, or there was damage to the boot area. If only one system disk fails, then use CellCLI commands to recover. In the rare event that both system disks fail simultaneously, you must use the Exadata Storage Server rescue functionality provided on the Oracle Exadata Storage Server Software CELLBOOT USB flash drive.
References:http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E80920_01/DBMMN/maintaining-exadata-storage- servers.htm#GUID-710814E7-4691-49EE-95AD-726D2D6C5BFE
NEW QUESTION 17
Which two are true about sparse griddisks and their use in disk groups on an X5 Exadata Database Machine?
- A. Sparse diskgroups must be created using sparse griddisks.
- B. Sparse diskgroups may be created using a combination of sparse and non-sparse griddisks.
- C. Sparse diskgroups may not be used for database snapshots.
- D. Additional space for a sparse griddisk is allocated as soon as newly written data is stored in the flashcache on a cell.
- E. The virtual size of a sparse griddisk may exceed the physical size of the space occupied by the griddisk.
Answer: AE
Explanation:
A: A sparse ASM disk group is composed of sparse grid disks.
E: Sparse grid disks allocate space as new data is written to the disk, and therefore have a virtual size that can be much larger than the actual physical size. Sparse grid disks can be used to create a sparse disk group to store database files that will use a small portion of their allocated space. Sparse disk groups are especially useful for quickly and efficiently creating database snapshots on Oracle Exadata. Traditional databases can also be created using a sparse disk group.
References:
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E80920_01/SAGUG/exadata-storage-server- snapshots.htm#SAGUG-GUID-42945059-13FD-4F6A-B7FA-A1201D16238F
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E80920_01/DBMSO/exadata-whatsnew.htm#DBMSO22120
NEW QUESTION 18
Identify two valid reasons for executing an X5 Exadata storage server rescue procedure.
- A. Accidental loss of all data from all griddisks in a storage server
- B. Corruption in the /(root) filesystem
- C. Corruption in a normal or high redundancy ASM diskgroup
- D. The failure of both physical disks 0 and 1
- E. Only the failure of physical disk 1
- F. Only the failure of physical disk 0
Answer: BD
Explanation:
The rescue procedure is necessary when system disks fail, the operating system has a corrupt file system, or there was damage to the boot area. If only one system disk fails, then use CellCLI commands to recover. In the rare event that both system disks fail simultaneously, you must use the Exadata Storage Server rescue functionality provided on the Oracle Exadata Storage Server Software CELLBOOT USB flash drive.
NEW QUESTION 19
You are evaluating the performance of a SQL statement that accesses a very large table. You run this query: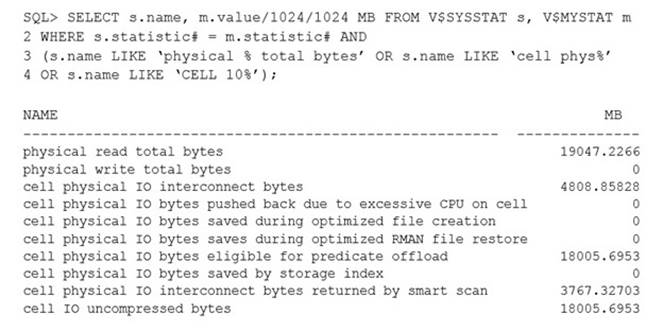
Identify two reasons why the “cell physical IO interconnect bytes” statistic is greater than the “cell physical IO interconnect bytes returned by smart scan” statistic.
- A. There is a transaction, which committed after the query began, that has modified some of the table blocks, causing some “cell single block physical reads” to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O.
- B. There are chained rows in the table, causing some “single block physical reads” to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O.
- C. The table is a hash clustered table, causing “cell multiblock physical reads” to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O.
- D. The table is list partitioned, causing “cell list of blocks physical reads” to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O.
- E. There is a local index on a list partitioned table on the column used in the WHERE clause, causing “cell list of blocks physical reads” to be requested by the database instance, resulting in additional I/O.
Answer: CD
Explanation:
C: Scan on a clustered table can prevent a Smart Scan from occur.
D: Scan on an index-organized table can prevent a Smart Scan from occur.
Note: The Cell physical IO interconnect bytes returned by smart scan metric shows how many bytes of I/O were returned by a smart scan to the database server.
References:https://uhesse.com/2011/01/19/exadata-part-i-smart-scan/
NEW QUESTION 20
You are patching your Exadata X6 Database Machine by applying a new image to the Storage Servers in a rolling fashion.
Your ASM environment on the Database Machine has five diskgroups stored on an unpartitioned Exadata storage grid, with redundancy settings as shown:
1. DATA_DBM1 – Normal Redundancy
2. RECO_DBM1 – Normal Redundancy
3. DBFS_DG – Normal Redundancy
4. DATA2_DBM1 – High Redundancy
5. DATA3_DBM1 • High Redundancy
Which two diskgroups will not suffer from any data loss throughout the patching process even if there is a single disk failure on one of the cells
- A. DBFS_DG
- B. DATA3_DBM1
- C. DATA2_DBM1
- D. DATA_DBM1
- E. RECO_DBM1
Answer: DE
Explanation:
HIGH redundancy provides protection against 2 simultaneous disk failures from 2 distinct storage servers or 2 entire storage servers. HIGH redundancy provides redundancy during Exadata storage server rolling upgrades.
References:http://blog.umairmansoob.com/choosing-high-vs-normal-redundancy-with- exadata/
NEW QUESTION 21
Your X6 Exadata Database Machine is running Oracle Database 12c, and has a large database with some very large tables supporting OLTP workloads.
High-volume insert applications and high-volume update workloads access the same tables.
You wish to compress these tables without causing unacceptable performance overheads to the OLTP workload.
Which three are true regarding this requirement?
- A. Compression is performed on database servers when using row store compress advanced in an Exadata environment.
- B. Using row store compress advanced will compress the data more than if using column store compress for archieve low.
- C. The compression method column store compress for archive high is the worst fit for this requirement.
- D. Compression is performed on Exadata Storage Servers when using row store compress advanced in an Exadata environment.
- E. Using row store compress advanced will compress the data less than if using column store compress forquery low.
Answer: ABD
Explanation:
A: Creating a Table with Advanced Row Compression
The following example enables advanced row compression on the table orders: CREATE TABLE orders ... ROW STORE COMPRESS ADVANCED;
B: ARCHIVE LOW compression (Exadata only), recommended for Archival Data with Load Time as a critical factor
NEW QUESTION 22
......
P.S. Easily pass 1z0-070 Exam with 90 Q&As Thedumpscentre.com Dumps & pdf Version, Welcome to Download the Newest Thedumpscentre.com 1z0-070 Dumps: https://www.thedumpscentre.com/1z0-070-dumps/ (90 New Questions)